Your Journey to Dynamics 365 Starts Here!
Fill in your business details and let
us be your partner in growth.
Evolution and purpose of ERP systems.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses aiming to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. By integrating various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relations into a unified system, ERP solutions provide a holistic view of business processes, enabling better decision-making and improved productivity.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses aiming to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. By integrating various functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer relations into a unified system, ERP solutions provide a holistic view of business processes, enabling better decision-making and improved productivity.
Despite these benefits, ERP implementation can be challenging. Approximately 75% of ERP projects fail to meet their objectives, highlighting the importance of careful planning and execution. However, for those that succeed, the rewards are substantial: 68% of organizations report revenue growth due to cloud-based ERP systems, and 63% notice a reduction in operational costs.

ERP systems integrate various functions into one complete system to streamline processes and information across the organization. This integration ensures that data flows seamlessly between different departments, providing a single source of truth and eliminating data silos. Modern ERP systems often leverage technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to enhance automation and provide deeper insights.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore all the aspects of ERP systems in detail including their application, history, benefits, challenges, and a lot more that will be provided episode-wise. So, let’s cut to the chase and get into the brief history of ERP systems first.
The history of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems is quite fascinating and spans several decades. Here’s a brief overview:

1. 1960s - Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
The roots of ERP can be traced back to the 1960s with the development of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems. These early systems were designed to manage manufacturing processes, particularly inventory control and production planning.
2. 1970s – Evolution of MRP
During the 1970s, MRP systems evolved to include more sophisticated features, such as production scheduling and procurement management. These systems were primarily used by large manufacturing companies.
3. 1980s – Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)
The 1980s saw the introduction of Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II), which expanded the scope of MRP to include additional functions like quality control, equipment maintenance, and financial management. This marked a significant step towards integrating various business processes.
4. 1990s – Emergence of ERP
The term 'ERP' was coined by Gartner in the 1990s to describe systems that integrated a wide range of business functions beyond manufacturing, including finance, human resources, and sales. This decade also saw the rise of major ERP vendors like SAP, Oracle, and JD Edwards.
5. 2000s – ERP II and Cloud ERP
The 2000s introduced ERP II, which incorporated additional functionalities such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Business Intelligence (BI). The advent of cloud computing also led to the development of cloud-based ERP systems, making ERP more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
6. 2010s to Present – Intelligent ERP (iERP)
Modern ERP systems, often referred to as Intelligent ERP (iERP), leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to provide real-time data insights and automation.
ERP systems have come a long way from their early days of managing inventory to becoming comprehensive solutions that streamline and optimize various business processes across industries.
Key features and popular ERP solutions
What is an ERP?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It’s a type of software system that helps organizations automate and manage core business processes for optimal performance. ERP software integrates various functions like finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, services, procurement, and more into a single system.
Here are some key reasons that justify the usage of ERP systems:
ERP systems can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or as a hybrid solution, depending on the organization’s needs.
What are the Different Components of ERP?
ERP systems are composed of various components, often referred to as modules, each designed to handle specific business functions. Here are some of the main components:

1. Accounting and Financial Management
Manages financial transactions, budgeting, and financial reporting. It includes tools for accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, and financial analytics.
2. Human Resources (HR)
Handles employee management, payroll, recruitment, performance evaluation, and benefits administration. It centralizes employee data and streamlines HR processes.
3. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Manages customer interactions, sales, and marketing activities. It helps in tracking customer data, improving customer service, and driving sales growth.
4. Inventory and Material Management
Tracks inventory levels, manages stock, and optimizes inventory control. It ensures materials are available when needed and reduces stockouts.
5. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Overseas procurement, production, and distribution processes. It helps in managing the supply chain efficiently, from vendor selection to order fulfillment.
6. Project Management
Assists in planning, executing, and monitoring projects. It includes tools for resource allocation, project tracking, and timeline management.
7. Data Analytics and Reporting
Provides insights and reporting capabilities to support decision-making. It enables businesses to analyze data, generate reports, and visualize key performance indicators.
8. Business Intelligence (BI)
Enhances data analysis and reporting, providing real-time insights and visualizations to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
These components work together to create a unified system that improves operational efficiency, data accuracy, and collaboration across departments.
What are Some of the Most Popular ERP Solutions with Their Strengths and Weaknesses?
Here are some of the most popular ERP solutions, along with their strengths and weaknesses:
1. SAP ERP
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
2. Oracle ERP Cloud
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
3. Microsoft Dynamics 365
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
4. NetSuite
Strengths:
Weaknesses
5. Sage ERP
Strengths:
Weaknesses:
Each of these ERP solutions has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of businesses and industries.
Learn about the cloud, on-premises, and hybrid ERP types.
Choosing the right ERP system for your business can be a complex decision, but understanding the different types available can help you make an informed choice. Here are the main types of ERP systems and some tips on how to choose between them:
Six Different Types of ERP Systems
1. Cloud-based ERP
2. On-premises ERP:
3. Hybrid ERP:
4. Industry-specific ERP:
5. Open-source ERP:
6. Small Business ERP:
Understand the reasons for using cloud ERP.
MSFT Power BI is a suite of business analytics tools that enables end users to visualize, analyze, and share data in a way that's easy to understand and act upon.
1. Cost Efficiency
Lower Initial Costs
Cloud ERP systems typically have lower upfront costs compared to on-premises solutions, as they eliminate the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure1.
Subscription Model
They operate on a subscription basis, which can help manage cash flow more effectively by spreading costs over time.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Easily Scalable
Cloud ERPs can easily scale up or down based on your business needs, allowing you to add or remove users and functionalities without significant disruptions.
Flexibility
They offer the flexibility to access the system from anywhere, on any device, which is particularly beneficial for remote work environments.
3. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Regular Updates
The cloud provider handles all updates and maintenance, ensuring that you always have access to the latest features and security patches without any downtime.
Reduced IT Burden
This reduces the burden on your internal IT team, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
4. Enhanced Security
Advanced Security Measures
Cloud ERP providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards.
Disaster Recovery
They also offer robust disaster recovery solutions, ensuring your data is safe and can be quickly restored in case of an emergency.
5. Improved Accessibility and Collaboration
Real-time Access
Employees can access real-time data and insights from anywhere, facilitating better decision-making and collaboration across different departments.
Unified Data
Cloud ERPs centralize data from various business functions, providing a single source of truth and reducing data silos.
6. Integration Capabilities
Seamless Integration
Cloud ERPs can easily integrate with other cloud applications, such as CRM, HR, and supply chain management systems, enhancing overall business efficiency.
APIs and Connectors
They often come with APIs and pre-built connectors that simplify the integration process.
7. Enhanced Analytics and Reporting
Built-in Analytics
Many cloud ERPs come with built-in analytics and reporting tools that provide valuable insights into business performance and help in strategic planning.
Machine Learning
Some systems incorporate machine learning and AI to offer predictive analytics and automate routine tasks.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Support
Regulatory Compliance
Cloud ERP providers ensure their systems comply with various regulatory requirements, helping your business stay compliant with minimal effort.
Audit Trails
They provide detailed audit trails and reporting capabilities to support compliance and governance.
Switching to a cloud-based ERP can significantly enhance your business operations, making them more efficient, secure, and adaptable to changing needs.
Keeping up to date with these changes can help you take advantage of new cost-saving opportunities.
Factors for selecting an ERP system.
Selecting the right ERP system is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and growth. Here’s a detailed guide to help you through the process:
1. Compliance and Regulatory Support
Identify Pain Points
Understand the specific challenges your business faces. This could be inefficiencies in inventory management, financial reporting, or customer relationship management.
Define Goals and Objectives
Set clear, measurable goals for what you want to achieve with the ERP system. Use the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to define these goals.
2. Explore ERP Options
Deployment Models
Decide between on-premises and cloud-based ERP solutions. On-premises solutions offer more control but require significant IT resources, while cloud-based solutions are more flexible and scalable.
Industry-specific vs. General ERP
Choose between industry-specific ERPs, which offer tailored features for your sector, and general ERPs, which provide broader functionality.
3. Evaluate Key Features
Core Modules
Ensure the ERP includes essential modules like finance, inventory management, CRM, manufacturing, and supply chain management.
Customization and Flexibility
Look for systems that can be customized to fit your unique business processes and can scale as your business grows.
Integration Capabilities
Check if the ERP can integrate with your existing systems and third-party applications.
Mobile Accessibility and Cloud Compatibility
Ensure the ERP supports mobile access and cloud capabilities for remote work.
Security and Data Privacy
Verify that the ERP has robust security features and complies with data privacy regulations.
4. Choose the Right Vendor
Vendor Reputation
Research the vendor’s reputation, customer reviews, and case studies to ensure they have a track record of successful implementations.
Support and Training
Evaluate the vendor’s post-implementation support and training options to ensure your team can effectively use the ERP.
5. Plan for Implementation
Total Cost of Ownership
Consider all costs, including licensing, implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Implementation Timeline
Develop a realistic timeline for implementation, including milestones and deadlines.
Change Management
Prepare your team for the transition by communicating the benefits and providing necessary training.
6. Monitor and Optimize
Track Benefits
Continuously monitor the ERP’s performance against your initial goals and objectives.
Optimize Processes
Regularly review and optimize your business processes to ensure you’re getting the most out of your ERP system.
By following these steps, you can select an ERP system that aligns with your business needs and supports your long-term growth.
Learn about ERP advancements and modular benefits.
The Future of ERP
The future of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is quite exciting, with several key trends and advancements shaping its evolution:
1. Cloud ERP
More businesses are moving to cloud-based ERP systems due to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. This shift allows for easier updates, better disaster recovery, and improved remote access.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being integrated into ERP systems to automate routine tasks, provide predictive analytics, and enhance decision-making processes. These technologies help in optimizing operations and personalizing user experiences.
3. Integration with IoT and Blockchain
The Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain are being incorporated into ERP systems to improve data accuracy, enhance security, and streamline supply chain management. IoT devices can provide real-time data, while blockchain ensures secure and transparent transactions.
4. Mobile Access and Remote Work
With the rise of remote work, ERP systems are becoming more mobile-friendly, allowing employees to access critical business information from anywhere. This trend supports a more flexible and distributed workforce.
5. Sustainability and Green ERP
There is a growing focus on sustainability, with ERP systems being designed to help businesses track and reduce their environmental impact. This includes managing resources more efficiently and complying with environmental regulations.
6. Enhanced Security
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, ERP systems are incorporating advanced security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates, to protect sensitive business data.
These trends indicate that ERP systems will continue to evolve, becoming more intelligent, integrated, and user-friendly, ultimately helping businesses operate more efficiently and effectively.
The Benefits of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a wide range of benefits for businesses. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Centralized Data Management
ERP systems consolidate data from various departments into a single database, ensuring that everyone in the organization has access to the same, up-to-date information. This eliminates data silos and reduces the risk of errors.
2. Improved Efficiency
ERP systems streamline business processes by integrating various functions like finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain into a single system. This reduces the need for manual data entry and helps eliminate repetitive tasks.
3. Enhanced Data Accuracy
With a centralized database, ERP systems ensure that all departments have access to the same, up-to-date information. This improves data accuracy and consistency across the organization.
4. Better Decision-making
ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics, which help managers make informed decisions quickly. The ability to generate comprehensive reports and insights is a significant advantage.
5. Scalability
As businesses grow, ERP systems can scale to accommodate new processes, departments, and users. This flexibility supports business expansion without the need for a complete system overhaul.
6. Cost Savings
By automating routine tasks and improving process efficiency, ERP systems can lead to significant cost savings. They also help reduce errors and delays, which can be costly for businesses.
7. Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems often include features that help businesses comply with industry regulations and standards. This is particularly important in sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
8. Improved Collaboration
With all departments using the same system, communication and collaboration across the organization improve. This leads to better teamwork and more cohesive operations.
9. Customer Service
ERP systems can enhance customer service by providing employees with access to comprehensive customer information. This allows for quicker response times and more personalized service.
Implementing an ERP system can be a significant investment, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial costs.
What are the Different Modules of ERP Systems?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are composed of various modules, each designed to handle specific business functions. Here are some of the most common ERP modules:
1. Financial Management
This module manages accounting, financial reporting, and analytics. It tracks all financial transactions and helps with budgeting and forecasting.
2. Procurement
Handles purchasing processes, supplier management, and procurement analytics. It ensures efficient procurement of goods and services.
3. Inventory Management
Manages inventory levels, stock movements, and warehouse operations. It helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels and reducing carrying costs.
4. Supply Chain Management
Oversees the entire supply chain, including logistics, order management, and supplier coordination. It aims to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce costs.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Manages customer interactions, sales processes, and customer service. It helps in improving customer satisfaction and sales performance.
6. Human Resources (HR)
Handles employee information, payroll, recruitment, and performance management. It streamlines HR processes and improves employee management.
7. Manufacturing
Manages production planning, scheduling, and quality control. It helps in optimizing manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality.
8. Project Management
Tracks project progress, resources, and costs. It ensures projects are completed on time and within budget.
9. Sales and Marketing
Manages sales orders, pricing, and marketing campaigns. It helps drive sales and improve marketing effectiveness.
10. Warehouse Management
Oversees warehouse operations, including picking, packing, and shipping. It aims to improve warehouse efficiency and accuracy.
These modules can be customized and integrated based on the specific needs of a business, providing a comprehensive solution for managing various business processes.
Implementation steps and overcoming challenges.
ERP Implementation: The Process
ERP implementation refers to the process of installing and configuring an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software system within an organization. This process integrates various business functions, such as finance, operations, and human resources, into a single system.
The goal of ERP implementation is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s business processes by providing real-time data and reporting capabilities. The process typically includes several phases:
Implementing an ERP system can be complex and time-consuming, but it can lead to significant benefits like increased productivity, cost savings, and improved data accuracy.
What are ERP Implementation Challenges?
Implementing an ERP system can be a complex and challenging process. Here are some common challenges organizations face during ERP implementation:
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, strong leadership, and ongoing support throughout the implementation process.
Strategies to Avoid Failures
What are ERP Implementation Strategies?
Implementing an ERP system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Here are some common ERP implementation strategies:
In this approach, the entire ERP system is deployed across the organization at once. This method can be efficient and allows for a quick transition, but it also carries higher risks if issues arise.
This strategy involves implementing the ERP system in stages, either by module, business unit, or geographical location. It reduces risk by allowing for adjustments along the way, but it can take longer to realize the full benefits.
With parallel adoption, the new ERP system runs alongside the old system for a period of time. This approach minimizes risk since the old system can serve as a fallback, but it can be costly and resource-intensive to maintain both systems simultaneously.
A pilot implementation involves deploying the ERP system in a small, controlled environment within the organization before a full-scale rollout. This allows for testing and troubleshooting in a real-world setting without impacting the entire organization.
Combining elements of the above strategies, a hybrid approach tailors the implementation process to the specific needs and constraints of the organization. This can provide a balanced approach, leveraging the benefits of multiple strategies.
Why Do ERP Implementations Fail?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) failures can be costly and disruptive but understanding the common causes and how to avoid them can help ensure a successful implementation. Here are some key reasons why ERP projects fail and strategies to prevent these issues:
Common Causes of ERP Failure:
Inadequate planning can lead to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and project fatigue. It’s crucial to set realistic expectations and create a detailed implementation plan.
Simply inserting new technology into old processes can hinder adoption. It’s important to redesign processes to align with the new ERP system.
Employees may resist new systems, leading to low adoption rates. Effective change management strategies, including clear communication and involving employees early, can mitigate this.
Without support from top management, ERP projects can lack direction and accountability. Engaging leadership early and ensuring they understand the project’s benefits is essential.
Insufficient testing before deployment can result in system failures post-implementation. Comprehensive testing phases are necessary to catch and resolve issues early.
How to Avoid ERP Failure?
Develop a detailed project plan that includes timelines, budgets, and resource allocation. Assign a dedicated project manager to oversee the implementation.
Ensure that new processes are designed to take full advantage of the ERP system. This may involve re-engineering workflows and training employees in new procedures.
Create a change management plan that includes frequent communication, training programs, and the establishment of ‘change champions’ within the organization.
Secure commitment from senior management and keep them involved throughout the project. Their support can drive the project forward and help overcome resistance.
Conduct extensive testing at various stages of the implementation to identify and fix issues before going live. This includes unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.
By addressing these common pitfalls and implementing these strategies, businesses can significantly increase their chances of a successful ERP implementation.
ERP's scope versus financial software features.
How Does ERP Work?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are designed to integrate and manage the core processes of a business. Here’s a breakdown of how ERP works:
ERP systems consist of various modules, each focusing on a specific business area such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, services, and procurement. These modules are interconnected and share a common database, ensuring that all departments have access to the same information.
All data within an ERP system is stored in a centralized database. This eliminates data silos and ensures that everyone in the organization is working with the same information. This centralization helps in maintaining a single source of truth for the business.
ERP systems automate many routine tasks, such as order processing, payroll, and inventory management. This automation reduces manual work, minimizes errors, and increases overall efficiency.
With ERP, businesses can access real-time data and generate reports quickly. This capability allows for better decision-making and more responsive management.
Modern ERP systems are scalable and can be customized to fit the specific needs of a business. They can be deployed on premises, in the cloud, or as a hybrid solution, depending on the company’s requirements.
By providing a unified platform, ERP systems facilitate better communication and collaboration across different departments and with external partners.
In essence, ERP systems streamline and optimize business processes, making it easier for companies to manage their operations efficiently and effectively.
Difference Between ERP and Accounting Software
The main difference between ERP and financials lies in their scope and functionality:
ERP System
ERP systems are comprehensive and integrate various business processes across an organization. They include modules for accounting, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), inventory management, and more.
ERP systems provide a unified view of enterprise data, enabling automation and insights across multiple departments. This helps in improving efficiency and decision-making.
Financials or Accounting Software
Financials, often referred to as accounting software, focus specifically on managing a company’s financial transactions and reporting.
Financial software handles tasks such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, payroll, and financial reporting. It is primarily used for bookkeeping and generating financial statements.
In summary, while financial software is a subset of ERP systems, ERP encompasses a broader range of business processes beyond just financial management.
Identifying when ERP becomes essential.
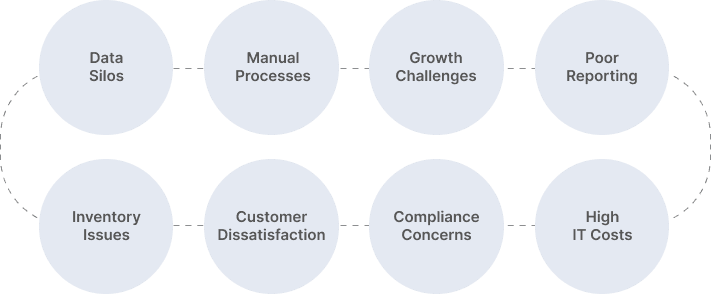
Top Signs You Need an ERP System
Implementing an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system can significantly streamline your business operations. Here are some signs that indicate you might need an ERP system:
How Does Dynamics 365 Contribute to Different Industries?
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a versatile platform that supports a wide range of industries by integrating customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) functionalities. Here are some key contributions across different sectors:
These are just a few examples of how Dynamics 365 can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries, enhancing productivity and customer satisfaction.
Here, you get yourself enlightened about the scope of Power BI for SMBs.
Here’s a comparison of some of the top ERP solutions, highlighting how Microsoft Dynamics 365 stands out:
| Feature/ERP Solution | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | SAP S/4HANA Cloud | Oracle NetSuite | Acumatica | SYSPRO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Versatile industries | Large enterprises | Mid-sized businesses | Small to mid-sized | Manufacturing |
| Deployment | Cloud, On-premises | Cloud, On-premises | Cloud | Cloud | Cloud, On-premises |
| Integration | Seamless with MS tools | Extensive | Comprehensive | Modular | Modular |
| Customization | Seamless with MS tools | Extensive | Comprehensive | Modular | Modular |
| Customization | High | High | High | High | High |
| User Interface | Intuitive | Complex | User-friendly | User-friendly | User-friendly |
| AI & Analytics | Advanced | Advanced | Advanced | Moderate | Moderate |
| Mobile Access | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pricing | Competitive | Premium | Premium | Competitive | Competitive |
| Customer Support | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive |
| Industry-Specific Solutions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Key Highlights of Microsoft Dynamics 365:
Suitable for a wide range of industries including manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and financial services.
Seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products like Office 365, enhancing productivity and user experience.
Leverages advanced AI and analytics to provide actionable insights and improve decision-making.
Highly customizable to meet specific business needs, ensuring a tailored solution.
Intuitive and easy to navigate, reducing the learning curve for users.
Scalable ERP solutions for businesses of all sizes.
No matter your business size, there’s an ERP out there claiming to fit your needs. But let’s be honest, not all ERPs are created equal. Let’s break it down:
Startups
As a startup, agility is your superpower, and you don’t want an ERP that slows you down. Sure, options like Zoho and QuickBooks can seem appealing—they’re lightweight and affordable. But here’s the catch: they’re often too basic. Dynamics 365 Business Central, on the other hand, grows with you. Need simple invoicing now but sophisticated inventory management next year? No problem. It’s like getting enterprise-level tools without overwhelming complexity.
Small Businesses
Scaling up means juggling more—more customers, more products, more headaches. Many small businesses gravitate towards Odoo or Sage Intacct. They’re decent, but integrations? Limited. Scalability? Questionable. Dynamics 365 doesn’t just scale; it streamlines. Picture real-time insights across sales, finance, and operations, all in one place. Plus, it’s Microsoft—so integrations with Office tools like Excel and Teams are seamless.
Medium-Sized Businesses
Now you’re competing with the big leagues. NetSuite often gets thrown around here, and while it’s solid, it’s also… rigid. Customizations can get expensive fast. Dynamics 365 offers flexibility without the hefty price tag. Whether you’re managing supply chains, forecasting demand, or diving deep into analytics, it’s tailored to handle complexity without sacrificing ease of use.
Large Enterprises
SAP and Oracle are popular options, but let’s be real, they’re often clunky and painfully costly. Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations delivers enterprise-grade power, but with unmatched usability. And because it’s part of the Microsoft ecosystem, collaboration across departments is effortless.
Bottom line: No matter your size, Dynamics 365 isn’t just an ERP—it’s the smarter, scalable, future-proof choice.
Differences and synergy between ERP and CRM.
ERP vs. CRM
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) are both essential software systems for businesses, but they serve different purposes and focus on different aspects of business operations.
| Aspect | ERP System | CRM System |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Manages and integrates core business processes, including finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and HR. | Manages a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. |
| Functionality | Centralizes data across departments; automates processes like order processing, inventory management, and payroll. | Tracks customer interactions, manages sales pipelines, and automates marketing campaigns. |
| Goal | Improves business operation efficiency by providing a single source of truth and better resource planning. | Enhances customer relationships, increases customer satisfaction, and drives sales. |
| Focus | Business-wide, integrating various processes. | Customer-centric, focusing on managing relationships. |
| Users | Used by multiple departments such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing. | Primarily used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams. |
| Data Management | Centralizes data from different business functions for a comprehensive view of operations. | Centralizes customer data to provide a complete view of customer interactions and history. |
ERP Integration
ERP integration is the process of connecting an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with other software applications, databases, or external systems to enable seamless data flow and synchronization across different business functions. This integration helps automate business processes, reduce data inaccuracies, and eliminate data silos, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
Key Benefits of ERP Integration:
It creates a single source of truth by consolidating data from various departments, improving communication and collaboration.
Integration facilitates automated data exchange, reducing manual entry errors and saving time.
Real-time data availability helps in making informed decisions quickly.
By integrating CRM systems, businesses can better understand and meet customer needs.
Common Integration Methods:
Tailored solutions using APIs to connect specific applications.
Prebuilt connectors provided by ERP vendors for popular applications.
Cloud-based platforms that manage and govern integrations.
Real-world applications across various industries.
Common Use Cases
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are versatile tools that can streamline various business processes across different departments. Here are some common use cases for ERP systems:
ERP systems can provide real-time updates on inventory levels, helping businesses avoid stockouts and overstock situations.
Automating the procurement process, from sending out requests for quotes to managing purchase orders, can save time and reduce errors.
ERP systems can help manage customer relationships, track sales pipelines, and automate marketing campaigns, leading to increased sales efficiency.
By tracking production schedules and inventory levels, ERP systems can optimize manufacturing processes and reduce downtime.
Automating accounting tasks and providing real-time financial insights helps businesses maintain accurate financial records and make informed decisions.
ERP systems can centralize customer data, making it easier to manage customer interactions and improve service quality.
ERP systems can streamline supply chain operations, from order processing to delivery, ensuring timely fulfillment and reducing costs.
Automating payroll, tracking employee records, and managing performance reviews can improve HR efficiency and employee satisfaction.
ERP systems can track project costs, resources, and timelines, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
These use cases illustrate how ERP systems can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve decision-making across various business functions.
Leveraging AI for smarter ERP and CRM systems.
Adopting AI in ERP and CRM systems can significantly enhance business operations and customer interactions. Here are some best practices to consider:
• Develop a long-term AI strategy that aligns with your business goals. This includes fostering a data-driven culture and ensuring relevant skills development.
• Start with pilot projects to understand the ROI and time to value before scaling up
• Ensure data integrity and security. Clean, accurate data is crucial for effective AI implementation.
• Regularly update systems to incorporate the latest AI innovations and trends.
• Train staff to effectively use AI tools. This includes understanding how to leverage AI for decision-making and process optimization.
• Use AI to automate repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
• Personalize customer engagements using AI-powered insights. This can include predictive sales and marketing strategies to better understand customer behaviors and preferences
• Implement AI-powered chatbots and automated workflows to enhance customer service3.
• Adhere to ethical AI principles, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI applications.
• Regularly review and adjust AI policies to align with evolving ethical standards and regulations.
• Integrate AI with scalable, flexible cloud platforms to handle large data volumes and drive operational efficiencies.
• Identify new use cases for AI and quickly deploy them to maintain a competitive edge.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively harness AI to transform their ERP and CRM systems, driving innovation, efficiency, and enhanced customer experiences.